Sainvet OEsol®
It is used only in animal health. You can find the product details below.


Composition:
OESOL; ear care solution, is transparent and fragrant and contains ethyl alcohol, boric acid, hydrogen peroxide and qsp water.
Properties:
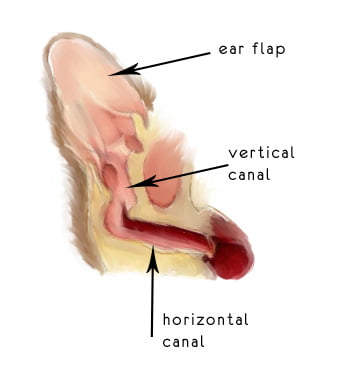
OESOL is an ear care solution for cats and dogs. It softens the dirt in and around the ear canal and provides easy cleaning and elimination of secondary factors.
Field of use
OESOL; It is used to support the ear canal problems of cats and dogs.
Storage and shelf life
It should be stored in a dry and cool place, protected from direct sunlight. The product should not be frozen. Shelf life is 2 years from the date of production.
Form of trade presentation
Sold in 30cc dropper glass bottles.
Label approval date: 15.11.2022
Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry Registration Date No: 15.11.2022 – 16/030
Usage and dosage
OESOL; For external use. Pour 0.5 ml of solution into the outer ear canal, massage it by hand, and clean it with cotton.
Method of Application:
- Week 1 to be applied once a day
- Week 2 to be applied once in 2 days
- CONTROL
- Week 3 to be applied once in 3 days
- Week 4 to be applied once in 4 days
- CONTROL
The frequency of application can be updated by the veterinarian during the control.
General warnings
It should not be mixed with other products. The recommended dose and duration should not be exceeded. Keep away from children. It can cause foaming and warming in the ear canal after application.
Precautions to be taken by the practitioner
Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, wash with plenty of water. In case of an allergic reaction, contact the nearest veterinary clinic.
In what situations can it be used?
- Allergy (food allergy, atopic dermatitis, contak)
- Parasites (Otodectes, Demodex, Sarcoptes)
- Autoimmune/immune-mediated (pemphigus foliaceus, vasculitis etc.)
- Endocrine Diseases (hypothyroidism, hyperadrenocorticism)
- Epithelialization diseases (sebaceous adenitis, zinc-derived dermatitis)
- Foreign body
- Glandular Diseases (sebaceous gland hyperplasia)
- Mushrooms (Aspergillus, candida)
- Viral (distemper)
- Hereditary (juvenile cellulitis)
- Bacteria (Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Pseudomonas, Proteus, etc.)
- Yeast (Malassezia)
- Drug reaction
- Epithelial changes (disruption of natural cleaning mechanism)
- Ear Canal (stenosis, edema, in-ear growths)
- Tympanum (rupture)
- Glandular (sebaceous hyperplasia)
- Pericartilago fibrosis or calcification
- Middle ear infection